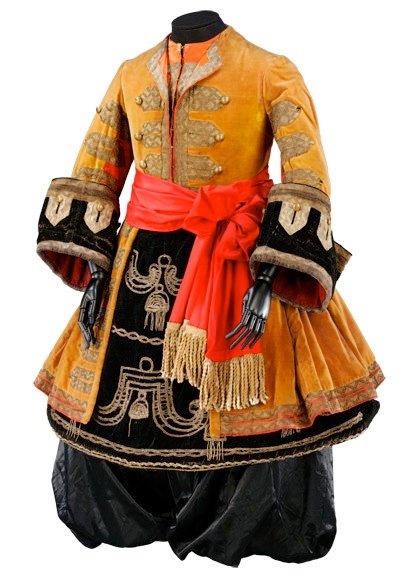
I went along to the Diaghilev exhibition at the V&A. He’s kind of an interesting figure to name an exhibition after, since he was an impresario, rather than an artist or designer, or even a composer or choreographer. But under his stewardship, the Ballets Russes really does seem to have been an extraordinary focal point for European culture. I’m a complete philistine about music and ballet, so none of the choreographers meant anything to me, and the only dancer I’d heard of was Nijinsky; but even I’ve heard of composers like Prokofiev, Satie and of course Stravinsky. And even I know that the first performance of The Rite of Spring is one of the significant cultural moments of the twentieth century.

And I’m slightly less of a philistine about art, so I’ve definitely heard of some of the people who designed sets and costumes for him: Pablo Picasso, Henri Matisse, Georges Braque, André Derain, Giorgio de Chirico, Natalia Goncharova, Coco Chanel. And apparently Joan Míro and Salvador Dalí as well, although neither of them featured in this exhibition. And that’s apart from some, like Léon Bakst, who are specifically known for their design work for the ballet. It is a hell of a list.
And it’s a fun exhibition: lots of cheery colours, and gorgeous costumes that have a battered glamour to them; and costume designs, which are often even more appealing than the costumes themselves. And the single largest item in the V&A collection: the back cloth for one of their ballets.

I also checked out the Raphael tapestries. Pope Leo X commissioned Raphael to design a set of tapestries with scenes from the lives of St Peter and St Paul, to hang in the Sistine Chapel, and one of the treasures of the V&A is the Raphael cartoons: i.e. the full size painted designs which the weavers worked from. To coincide with the current Pope visiting the UK, the Vatican has lent four of the actual tapestries to hang alongside the paintings for a bit.
And they’re quite interesting to see, although they have rather fallen victim to changing tastes. The Raphael cartoons have always been regarded as some of the most important bits of Renaissance art in Britain, but I don’t think I’m alone in finding them a bit unsympathetic. It’s not just the subject matter, although that doesn’t help; there’s something about these monumental groups of posed figures that is just a tiny bit, um, boring. Maybe it’s the self-conscious grandeur of them; these really are the Catholic equivalent of Socialist Realism. Then again, if Stalin had had people like Raphael and Michelangelo available, Socialist Realism might have been pretty fabulous.
» Top: costumes for female dancers in The Rite of Spring. Designed by Nikolai Roerich, 1913. Bottom: costume for a ‘Negro Lackey’ from The Sleeping Princess. Designed by Léon Bakst, 1921.